APIs
API stands for Application Programming Interface, and the building blocks of modern software because they allow for the sharing of resources and services across applications, organization's, and devices.
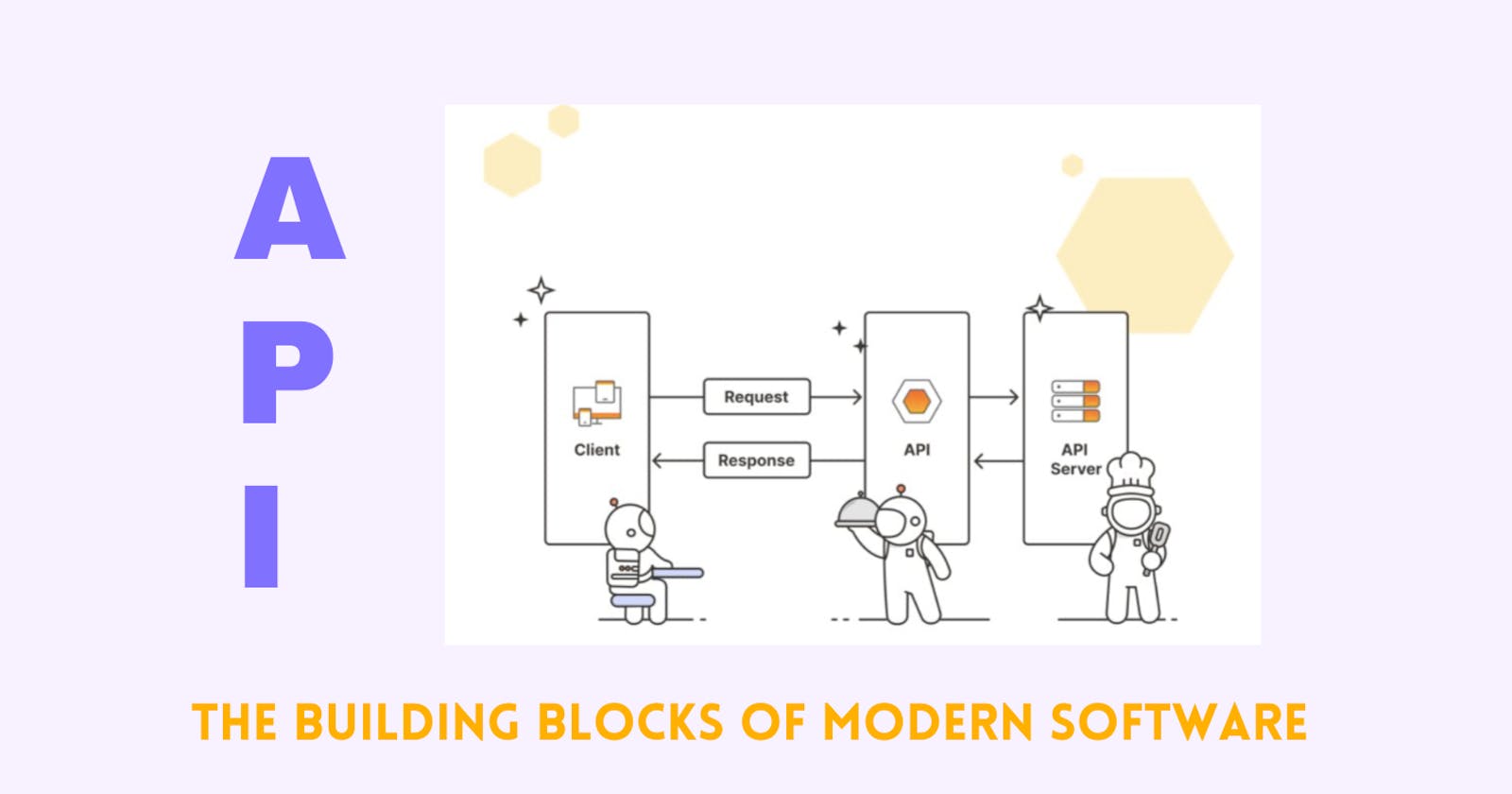
Networking Terms Used in API
| Term | Description |
| Client | The requester. (i.e. your browser or an app) |
| API | Simplified interface for interacting with the backend |
| Server | The backend where the processing happens |
Types of APIs
There are three types of APIs described below
Hardware APIs - Interface for software to talk to hardware.
Software Library APIs - Interface for directly consuming code from another code base.
Web APIs - Interface for communicating across code bases over a network.
Architecture For APIs
REST (Representational State Transfer) - Representational State Transfer, is a design pattern for building web services.
GraphQl - A query language and runtime for Building APIs
WebSocket - Protocol for bi-directional communication that allows data to be exchanged in real-time via a single, permanent connection.
Webhooks - Apps can communicate real-time data to other apps or services through automated notifications.
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) - a messaging protocol for exchanging structured data
gRPC (Google Remote Procedure Call) - Google created a high-performance, language-neutral RPC framework to facilitate effective inter-service communication.
MQTT (MQ Telemetry Transport) - Lightweight messaging protocol for IoT devices, emphasizing low bandwidth and battery usage.
How To Access APIs
There are three scopes of ways through which we can interact and use APIs
Public APIs (known as Open APIs) - Used by anyone who discovers the API
Private APIs - Used only within an organization and not made public
Partner APIs - Used between one or more organizations that have an established relationship
REST (Representational State Transfer):-Request methods
When we make an HTTP call to a server, we specify a request method that indicates the type of operation we are about to perform. These are also called HTTP verbs.
Some common HTTP request methods correspond to the CRUD operations mentioned earlier. you may check more on MDN web documentation
| Method name | Operation |
GET | Retrieve data (Read) |
POST | Send data (Create) |
PUT/PATCH | Update data (Update) |
DELETE | Delete data (Delete) |
Request URL
In addition to a request method, a request must include a request URL that indicates where to make the API call. A request URL has three parts:
Protocol - such as
http://orhttps://Host - location of the server
Path - route on the server
| Protocol | Host | Path (API endpoints) |
https:// | www.linkedin.com | in/mohd482/ |
Response status codes
Whenever we send any request through API, we get some status about the response we get from any server or API provider. Some of them I have explained below:-
| Code range | Meaning | Example |
1xx | Informational | 100 - Continue |
2xx | Success | 200 - OK |
3xx | Redirection | 302 - Found |
4xx | Client errors | 400 - Bad Request |
5xx | Server errors | 500 - Internal server error |
Till now you have understood what are APIs, their types, architectures how to access them and their request methods now let's understand what is Postman.
Introduction To Postman
Postman is an API platform for building and using APIs. Postman simplifies each step of the API lifecycle and streamlines collaboration so you can easily create better APIs and consume them.
You can learn to use Postman by completing its course named Postman API Fundamentals Student Expert Certification, through this course you'll get to know how to create and use the APIs.
API Testing Tools:
Postman
Apigee
JMeter
Ping API
Soap UI
vREST
How to Create APIs?
Creating an API is easy unless you are very clear on the basic concepts. It’s an iterative process (based on feedback) that includes a few easy steps:
Plan your goal and the intended users
Design the API architecture
Develop (Implement the code) and Test API
Monitor its working and work on feedback
Conclusion:-
APIs are the foundation of modern software, enabling the sharing of resources and services across applications, organizations, and devices. APIs can be accessed through public, private, or partner APIs. Postman is an API platform that simplifies the API lifecycle and streamlines collaboration. Postman's API Fundamentals Student Expert Certification course provides a comprehensive understanding of API creation and usage.
Follow Me On Socials :
Like👍|Share📲|Comment💭